HIGHWAY ENGINEERING(Part 3)
(
SIGHT DISTANCE
- What is Sight Distance?
- What is the factor affecting Sight Distance?
(ii) Driver's Reaction Time- The reaction time is taken by the driver from the instant of seeing the object to the instant when the brakes are applied.
(iii) Brake's Efficiency- Efficiency of brakes depends upon the age and the characteristic of vehicle.
(iv) Gradient of Pavement- Gravitational force comes into action which causes the vehicle to take more time to stop the vehicle means more sight distance is required.
(v) Frictional Resistance- Less distance required by vehicle to stop when frictional resistance is more.
- Stopping Sight Distance-
Stopping sight distance composed two components-
(i) Lag Distance(d)- It is the distance travel by the vehicle in total reaction time.
- Lag Distance(d)= vt metres ( v= design speed in m/s t= total reaction time in sec)
- Lag Distance(d)= 0.278vt metres ( v= design speed in kmph t= total reaction time in sec)
- Braking Distance(l) = (v^2/2gf) (f= coefficent of friction v= design speed in m/s)
- Braking Distance(l) = (0.278v^2/2gf) (f= coefficent of friction v= design speed in kmph)
Stopping Sight Distance(SSD)= (vt + v^2/2gf). (v= design speed in kmph)
- Overtaking Sight Distance-
MEASUREMENT OF OVERTAKING SIGHT DISTANCE
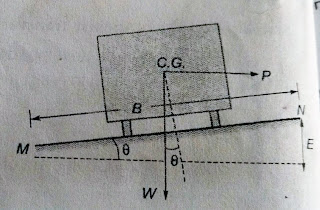
SUPERELEVATION
Superelevation is the distance between the height of inner and outer edges of highway pavement.
In passing from a straight to a curve path, there should be two forces-
(i) the weight of the vehicle.
(ii) the centrifugal force.
SUPERELEVATION IN PAVEMENT SECTION
Superelevation(e)= tanθ= E/B
- Relation between superelevation(e), coefficent of friction(f) and centrifugal ratio-
e + f = v^2/gR ( Here, v = kmph)



ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon